Home » Medical Aesthetix
Category Archives: Medical Aesthetix
What Botox Can Do For Your Bladder
Botox San Diego is a cosmetic injectable that temporarily reduces or eliminates facial fine lines and wrinkles. It was originally developed to treat blepharospasm and strabismus but is now used for many different purposes.
The toxin in botox blocks nerve signals from reaching the muscles in which it is injected, causing them to relax. Typically, the results last 3 to 6 months.
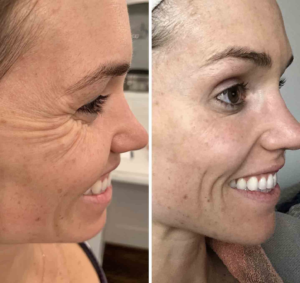
Many people are perfectly content with their wrinkles and don’t feel the need to spend money or time smoothing them out. Others, however, would prefer a more youthful appearance and are willing to take steps to do so. These can include dietary changes, lifestyle modifications (such as avoiding sun exposure and quitting smoking), and cosmetic treatments like laser therapy and dermal fillers. Botox is a popular option that reduces fine lines and wrinkles by temporarily paralyzing the muscles that cause them. Its effects are typically seen within a week and last for about three to four months.
The most common areas treated by Botox are frown lines, forehead creases, and crow’s feet near the eyes. The injectable is also effective at reducing lip lines, thick bands in the neck and gummy smiles.
Lines and wrinkles come about when collagen, a protein found in deep facial layers, begins to thin. This is caused by aging, sun damage and other factors, and results in the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. Botox works by injecting a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, a neuromodulator that blocks nerve signals and relaxes the muscles to smooth out fine lines and wrinkles.
Botox works best on dynamic wrinkles, which appear as a result of repetitive facial expressions such as smiling, squinting and frowning. The injections target the facial muscles that are responsible for causing these wrinkles and temporarily paralyze them, softening their appearance.
Static wrinkles, on the other hand, are those that remain visible when you are not making any facial expressions. These are not as responsive to Botox treatment and can usually be addressed with dermal fillers or other cosmetic treatments.
In addition to reducing fine lines and wrinkles, Botox has been used to treat a variety of conditions including neck spasms, migraines and facial spasms caused by Bell’s palsy. It has also been effective in treating strabismus, the condition that causes one eye to drift from its correct position. Lastly, it is also being used to treat patients with cervical dystonia, a painful condition that affects the muscles in the neck and can cause uncontrolled muscle movement such as head tilting or eye twitch.
Overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms, such as frequent trips to the bathroom and urine leaks, can be a serious issue for some people. Botox can relieve OAB symptoms by temporarily paralyzing the bladder muscle. This treatment is an option if lifestyle changes and medications don’t provide relief. It’s a good idea to talk to your doctor before getting Botox for your bladder, as the medication is not right for everyone.
OAB occurs when nerve signals tell the bladder that there’s a strong need to pee, which causes the bladder muscles to squeeze too often and intensely, leading to urinary urgency and leaking. OAB Botox treatment works by blocking those nerve signals that lead to the bladder spasms, reducing your symptoms and helping you feel better about your quality of life.
Bladder Botox is a quick, minimally invasive treatment that’s done in the office under local anesthesia. After the lining of your bladder is numb, your doctor will use a scope to look inside your bladder and then inject the Botox into the muscle of your bladder. The injections take about five minutes or less. Your doctor will also give you a short-term antibiotic to prevent an infection after the procedure.
After your treatment, you’ll need to avoid rubbing or pressing on the area where the injections were done for about 12 hours. You should also stay upright or avoid lying down during this time. You can usually resume normal activities after this period. If you experience any bruising or pain at the injection site, it should go away within a day. You may also notice a slight burning sensation when you urinate, which should go away within a few days.
You’ll need to get your Botox treatments every three or four months to keep your OAB symptoms under control. Eventually, your muscles will train themselves to contract less, and you’ll need to get the injections less frequently. It’s best to schedule your treatments with your urologist, who will be able to give you an accurate timeline based on your unique needs.
The Botulinum toxin has a long list of medical uses, including treating chronic migraines, specific bladder issues and excessive sweating. It is injected into the affected muscles, where it blocks nerve signals that cause them to contract. It is a prescription medicine that must be administered by a licensed and trained health care professional.
Your doctor will decide which type to use to treat your condition. It is important to note that one botulinum toxin type cannot be used interchangeably with other types. They have different potencies once the contents of each vial are dissolved, and using them in combination could lead to an insufficient or unwanted effect.
Before a Botox injection, your healthcare provider will cleanse the area and may mark it with a pen or marker to guide the needle. A topical numbing cream may be applied to help minimize discomfort. Then, your injector will administer the injections. It usually takes just a few minutes. You can go home soon afterward.
Injections usually cause only mild discomfort, but the exact sensations depend on the affected muscles and the site. Some people feel prickling or pressure, while others experience a headache. It is important to avoid exercise, facials, and laser treatments for one to two days after treatment to reduce the risk of toxins being dislodged and traveling to areas where they are not needed.
Botox is not recommended if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. It also should not be used by individuals who have an infection in the treated area. Some medications can increase your risk of bruising and redness at the injection sites, so be sure to discuss any current medications with your healthcare provider.
If you suffer from chronic migraines or other medical conditions, talk to your healthcare provider about whether botox might be right for you. This is a safe, effective treatment that can significantly improve your quality of life. The most common substantive complication of botox is the temporary weakness of a muscle, which resolves once the injection has worn off. A precise knowledge of functional anatomy and experience with this technique are necessary to achieve optimal results.
A squint, also known as strabismus, is a condition where your eyes don’t align properly. When you look at an object, six different muscles work in tandem to direct each eye towards that object. In someone with strabismus, these muscles don’t work together, which causes one eye to turn in (esotropia) or out (exotropia) or up or down (hypertropia).
It can be caused by any number of things. In some cases, it’s a genetic defect. In others, it’s caused by eye injuries or other conditions such as cataracts. It can occur all the time or just sometimes.
Your eye care provider will do a physical exam to see how much your child’s eyes are misaligned. He or she may then do additional tests to determine what is causing the strabismus. This can include a prism test, in which a clear wedge-shaped lens is placed in front of the deviating eye. This forces the brain to use the weaker eye, and it helps correct the strabismus.
If your child’s squint is caused by a nerve disorder, he or she may benefit from a botox injection. The drug temporarily weakens the muscles in the affected area, which can relieve the symptoms of strabismus and restore proper muscle balance.
Before recommending treatment, your child’s ophthalmologist will conduct a complete eye examination, including a detailed examination of the internal structures of the eyes, as well as an evaluation of his or her visual acuity and depth perception. Other treatments for strabismus include glasses, orthoptic exercises, occlusive patching and surgery.
Botox is made from a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum, which is a naturally occurring toxin that has been refined for medical use. It has many therapeutic uses, and it is a safe and effective treatment for a variety of conditions. However, it is important to discuss this treatment with your doctor before receiving the injection, especially if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. There is a small chance that the medicine can pass through the placenta and affect your unborn child. It is also not recommended for patients with certain medical conditions, such as a bladder infection or severe allergies.